Introduction
Carbon fiber has revolutionized the world of high-performance materials, significantly impacting various industries, from aerospace to automotive and sports equipment. Among these, the cycling industry has seen remarkable advancements, particularly in the design and performance of rims.
Carbon fiber has played a pivotal role in enhancing rim performance, offering a combination of strength, lightness, and durability that surpasses traditional materials. This article explores the different carbon fiber wheels that are available.
It is important to understand that these weaves do not to any significant extend affect the performance of bicycle rims, as they are only used in the top layer. Aside from the top layer, carbon bicycle rims all use unidirectional carbon fiber, therefore in this article, the focus will be on UD (unidirectional) carbon fiber, while touching on the other carbon fiber weaves.
Types of Carbon Fiber Weaves
Unidirectional (UD) Weave
The unidirectional (UD) weave consists of carbon fibers aligned parallel in a single direction, offering the highest strength and stiffness along the fiber’s length. This weave is ideal for applications requiring maximum tensile strength and stiffness in one direction, such as in high-performance road racing bike rims. In fact, this is the primary type of weave used in carbon bicycle rims.
However, the rigidity is predominantly in the fiber direction, making it less effective in providing torsional rigidity and resilience against impacts from other angles. This limitation means that while UD weave excels in direct load applications, it may not be as versatile in handling multi-directional stresses, such as on bicycle frames.
Elitewheels has its own in-house unidirectional carbon fiber that we call UNI. It uses genuine Japanese Toray T800 and T1000 carbon fiber to create our Drive road and gravel wheels, which are not only stiff and strong, but also lightweight.
Twill Weave
Twill weave is characterized by a diagonal pattern where the fibers are woven in a staggered manner, providing a unique aesthetic appeal alongside functional benefits. This weave offers a unique and attractive appearance that makes it stand out from traditional 3K, 6K, 12K, and UD.

3K Weave
The 3K weave consists of tows with 3,000 filaments each, striking a balance between weight and strength. This is one of the most common weaves and is found on wheels from many popular brands.
6K Weave
With tows containing 6,000 filaments each, the 6K weave stands out more, as the weave is more visible. 6K weaves are relatively uncommon. Most rims feature either UD, 3K, or 12K options
12K Weave
The 12K weave uses tows with 12,000 filaments. This offers a striking appearance. It makes the rim stand out much more and clearly shows off the classic carbon fiber look.
Satin Weave
Satin weave is a more complex pattern where fibers pass over multiple other fibers before weaving under, creating a smooth and flexible fabric. It has a distinctive look that many find more visually appealing.
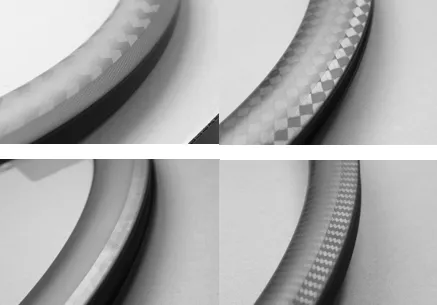
Performance
Lateral Stiffness
UD carbon fiber, with all fibers aligned in a single direction, provides maximum stiffness along this axis. This one-dimensional reinforcement ensures the material exhibits the highest stiffness in the direction of the fibers, making it particularly effective in resisting deformation under loads aligned with this axis. This lateral stiffness is important for power transfer, allowing for a more efficient wheelset. Many of our Drive road and gravel wheels use replaceable carbon spokes, allowing them to be even stiffer than traditional wheels.
Torsional Rigidity
UD carbon fiber exhibits less torsional rigidity because its single-directional fiber alignment lacks reinforcement against perpendicular forces.
Resilience to Impact
UD carbon fiber has moderate impact resilience. Its lack of cross-directional fibers marginally limits its ability to absorb and distribute impact forces effectively. All of our Drive road and gravel wheels have passed the UCI vertical impact test, allowing them to be used in professional races.
Production Costs
UD carbon fiber benefits from a simpler manufacturing process and lower production costs. Its straightforward production, involving less complexity, translates into reduced costs.
Plain weave carbon fiber incurs moderate production costs due to its crisscross weaving pattern, which is more complex than unidirectional but simpler than advanced weaves.
Twill weave carbon fiber comes with a higher production cost. The intricate diagonal pattern requires more advanced weaving techniques and additional processing steps.
The 3K weave has a moderate production cost, higher than plain weave but lower than 6K and 12K. The complexity of its weave pattern raises production costs compared to simpler weaves.
6K carbon fiber is more expensive to produce due to its higher filament count and denser weave. The advanced manufacturing techniques needed for this weave contribute to its increased production costs.
12K carbon fiber has the highest production cost. The complexity of weaving 12,000 filaments and the extensive processing involved lead to significantly higher costs compared to other weaves.
Benefits of Carbon Fiber Weaves
Weight Reduction
One of the most significant advantages of carbon fiber weaves is their ability to reduce weight without compromising strength. Unidirectional and 3K weaves are particularly effective in achieving this balance. Lightweight rims are crucial for cyclists as they reduce rotational mass, allowing for quicker acceleration and improved climbing efficiency. Using our in-house UNI carbon fiber, we are able to design lightweight wheelsets starting at just 1260 grams for our 40mm rim depth option.
Strength and Durability
Carbon fiber weaves enhance the strength and durability of rims. Unidirectional weaves provide maximum tensile strength, making the rims highly resistant to impact and stress fractures.
Stiffness and Responsiveness
The stiffness of a rim affects its responsiveness and power transfer. Unidirectional weaves are highly effective in providing stiffness along the direction of the fibers, making the rims exceptionally responsive to pedal input. This results in better power transfer and improved handling, especially during sprints and climbs.
Aesthetic Appeal
Beyond performance, carbon fiber weaves also offer aesthetic benefits. The distinct patterns of twill and plain weaves add a unique, high-tech look to the rims, making them visually appealing to cyclists who value both performance and style. Our rims feature our own unique finish. Our popular Drive road and gravel wheels use a special kind of marbling finish, though it is purely aesthetic.
ractical Applications and Considerations
Cost Considerations
While carbon fiber rims offer superior performance, they come at a higher cost compared to traditional materials like aluminum. Cyclists need to weigh the performance benefits against the cost to determine if carbon fiber rims are the right investment for their needs. Elitewheels produces all of its own rims, allowing for reduced costs, that we pass onto the consumer.
Conclusion
Carbon fiber offers cyclists a combination of lightweight, strength, stiffness, and aerodynamic benefits that are unmatched by traditional materials. By understanding the unique properties of carbon fiber weaves, cyclists can make informed decisions about their equipment, enhancing their riding experience and performance. As technology continues to advance, the future holds even greater potential for carbon fiber in revolutionizing the cycling industry.






